
High and low temperature alternating test chambers are composed of many components, each playing a critical role in the operation of the equipment. Today, we will focus on the heating element, providing a deeper understanding of this essential part of the testing device.
Working Principle of the Heating Element
Inside a high-temperature-resistant stainless steel seamless tube, high-temperature resistance wires are evenly distributed. The gaps are filled with crystalline magnesium oxide powder, which has excellent thermal conductivity and insulation properties. This structure ensures high thermal efficiency and uniform heat distribution. When an electric current passes through the resistance wires, heat is transferred through the magnesium oxide powder to the metal tube’s surface and then to the heated object or air, achieving the desired heating effect.
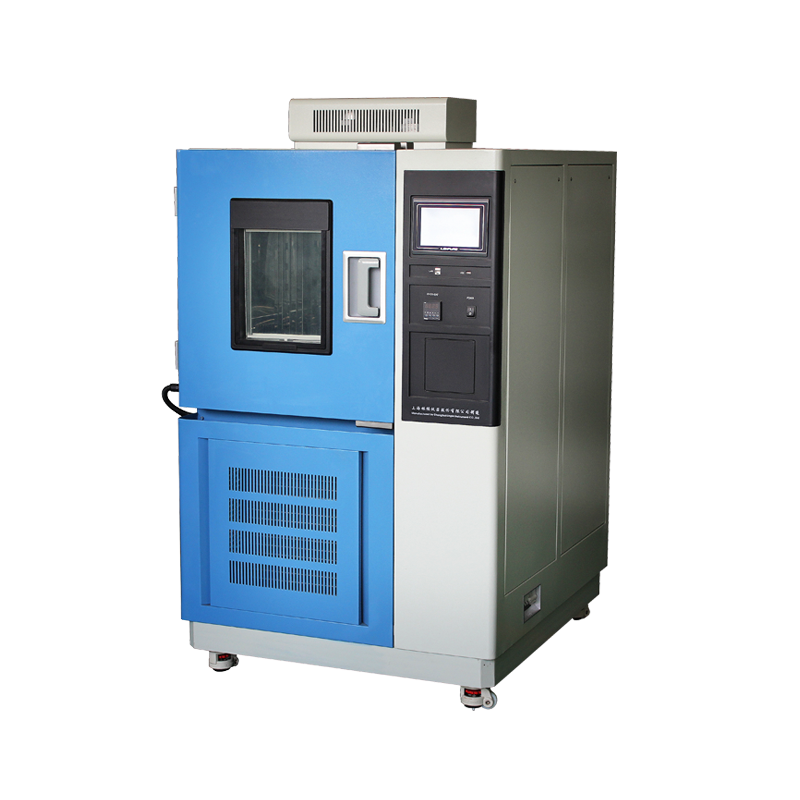

Key Precautions When Using Heating Elements
Carbon Buildup on the Surface
If carbon deposits form on the tube surface, they should be promptly removed to prevent reduced efficiency or component damage.
Melting Solid Oils (e.g., Paraffin, Asphalt)
When heating solid oils, reduce the voltage initially and only increase it to the rated level after melting to avoid overloading the element and shortening its lifespan.
Storage and Maintenance
Store the heating element in a dry environment. If the insulation resistance drops below 1 MΩ due to prolonged storage, it can be restored by:
Baking in an oven at 200°C for several hours, or
Running the element at a low voltage for a few hours.
Common Issue: Dry Firing of Heating Elements
Sometimes, heating elements in high and low temperature test chambers may experience dry firing, primarily due to:
Fan Failure: If the chamber’s fan stops working, heat cannot dissipate properly.
Proximity of Overheat Sensor: If the sensor is too close to the heating element, it may trigger false alarms. Adjust the distance accordingly.
Incorrect Gas Switch Setting: Open the control box’s side panel and check if the gas switch setting is correct (typically 50–80°C higher than the chamber’s temperature). Adjust if necessary.
Conclusion
The proper functioning of heating elements directly affects the test results of high and low temperature alternating test chambers. As a critical component, understanding its operation and maintenance ensures accurate and reliable testing.
For more information or equipment inquiries, please contact us at 400-066-2888. We provide high-quality testing chambers and professional support.