Environmental Test Chambers for IEC 60068 Part2-2 Testing B: Dry heat
Welcome to our website:http://www.lenpure.com/
Company Profile
Shanghai Linpin Instrument Stock Co., Ltd. is a reliable and professional high-tech enterprise in the field of environmental teat chambers. As an expert environmental test chambers manufacturer and a comprehensive one-stop solution service provider, Lenpure owns its standardized production bases and showrooms.

By virtue of innovated products, efficient supply chain and strong strategic executive force, Lenpure is specialized in creating premium, safe, eco-friendly, professional and highly-efficient service.
Lenpure offers a full range of standard or custom-designed environmental test chambers, which providing our customers with solutions to meet their all demanding environmental testing requirements. These environmental test chambers range from small bench top chambers to full walk-in test rooms. According to different test condition and requirement, our product could divide into different type as below:
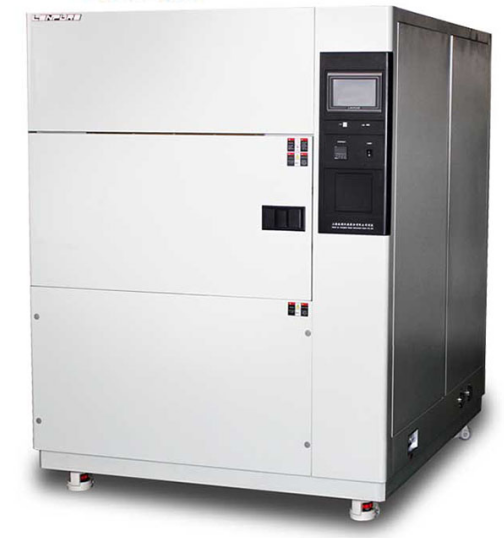
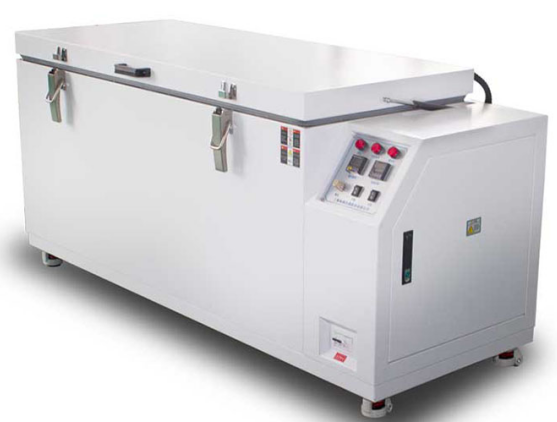
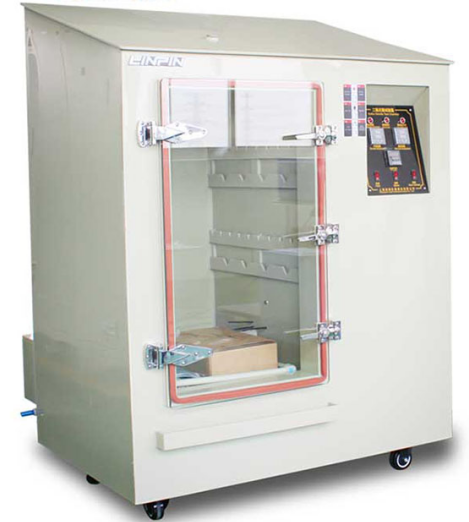
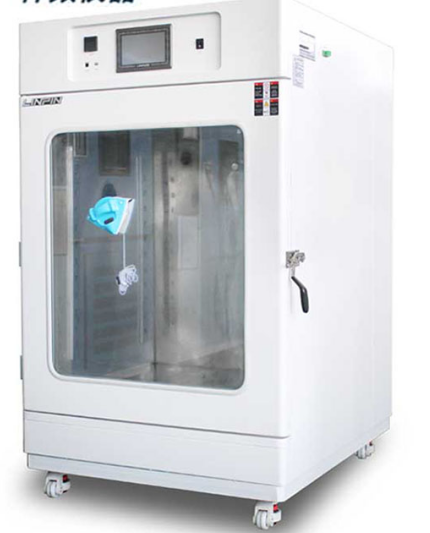















Insisting on high input on the R&D, innovating products.
Adhere to high investment in scientific research and creating differentiated products, Lenpure has gained lots of honor certificates thanks to its superior quality, design and performance which are widely praised by customers. Lenpure climatic chambers win a number of software copyright and technology patents, combining reliability, easy-to-use performance with practicality to meet all-round requirements from customers.
R&D team consists of experienced and skilled industry experts. Besides, Lenpure has established strategic partner relationship with Shagnhai Jiaotong University, and also has set up R&D centers in Beijing as well as Shanghai.
With Overseas Business Department and corresponding after-sales department set up, Lenpure has advanced sales system and after-sales service system.
Lenpure adheres to the development concept of ‘Tests-for the purpose of progress’ and efficient end-to-end service system and vertical management structure to ensure the policies from diversified and experienced management team are effective and in time. Persisting in innovation and excellent enterprise culture is our core competence.
Based on the industry advantages and scientific innovation, Lenpure will keep persisting in building up future-oriented environmental test chambers, and to create value to customers and society.
Now let me introduce the application of tests for non heating-dissipating specimens versus tests for heating-dissipating specimens to you.
This standard deals with dry heat tests applicable both to heat-dissipating and non heat dissipating specimens. For non heat-dissipating specimens. Tests Bb and Bd do not deviate essentially from earlier issues.
The obiect of the dry heat test is limited to the determination of the ability of components equipment or other articles to be used. transported or stored at high temperature.
These dry heat tests do not enable the ability of specimens to withstand or operate during the temperature variations to be assessed. In this case, it would be necessary to use IEC 60068.2-14 Test N: Change of temperature.

General
The environmental temperature test chambers shall be constructed and verified in accordance with specifications ICE 60068-3-7.
Further guidance for the dry heat and cold tests can be found in ICE 60068-3-1, and general guidance in ICE 60068-3-7.
A specimen is considered heat-dissipating only if the hottest point its surface, measured in free air conditions in more than 5K above the ambient temperature of the surrounding atmosphere after temperature stability has been reached. When the relevant specification calls for a storage or transportation test pr does not specify an applied load during the test, the dry heat test Bb will apply.
Ascertaining high or low air velocity in the test chamber
Under standard atmospheric conditions for measurements and test (see IEC 60068-1) with an air velocity <0,2 m/s, the specimen shall be switched on or electrically loaded as specified for the high temperature at which the test is to be carried out.When temperature stability of the specimen has been reached, the temperature of a number of representative points around or on the specimen shall be measured using a suitable monitoring device.
The temperature rise that occurs at each point shall then be noted.The chamber air flow is switched on and, once temperature stability has been achieved. the temperature of the representative points shall again be measured. If the temperatures differ from those measured without air flow by more than 5 K (or a value stated by the relevant specification) this value shall be noted in the test report and the test chamber is considered to have high velocity circulation. The specimen is then switched off and any loading conditions removed.
Application of tests with sudden change of temperature versus tests with gradual change of temperature
In Tests Bb, Bd and Be with gradual change of temperature, the specimen is introduced into the test chamber, the latter being at the laboratory temperature. The temperature in the chamber is then increased gradually so as to cause no detrimental effects on the test specimen due to the temperature change.
Testing of heat-dissipating specimens
Tests Bd and Be describe procedures for testing heat-dissipating specimens with low air velocity circulation. This is to allow localised hot spots to develop within the specimen similar to those that would appear in installed applications.
Temperature monitoring
The air temperature in the chamber shall be measured by temperature sensors located at such a distance from the specimen that the effect of the dissipation is negligible. Suitable precautions should be taken to avoid heat radiation affecting these measurements. For more.information see IEC 60068-3-5.
Packaging
For storage and transportation tests, equipment may be tested with its packaging in place.However, as these tests are steady state tests the equipment will eventually stabilise at chamber's temperature. Packaging shall be removed unless the relevant specification requires it to remain in place or heating elements are incorporated in the package.
Diagrammatic representations
To facilitate the choice of test method, a diagrammatic representation of the various procedures is given in Figure 1.
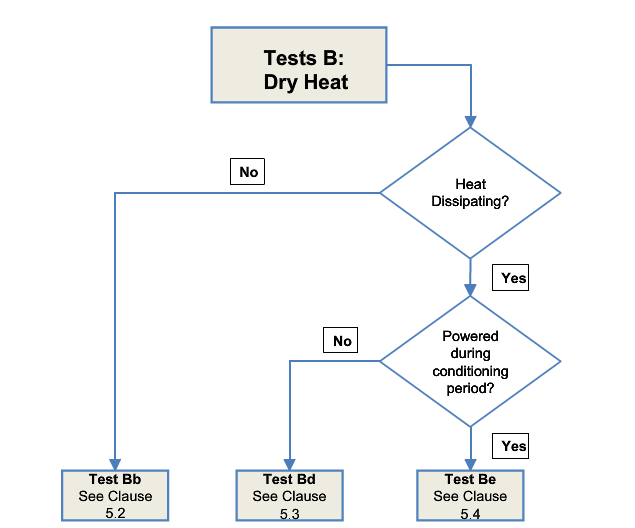
Test Procedure
Confirmation of performance
IEC 60068-3-5 provides guidance for the confirmation of performance of temperature test chambers. IEC 60068-3-1 provides general guidance for the performance of tests A and B. The chamber shall be large enough compared with the size and amount of heat-dissipation of the test sample.
Working space
The dimensions of the test sample shall be such that it is entirely within the working space of the test chamber.The temperature of the incident air delivered to the test specimen shall be within± 2 K of test severity temperature during the steady state conditions. The air temperature in the working space shall be measured in accordance with subclause 4.5.
NOTE: Where due to the size of the climatic chambers it is not feasible to maintain these tolerances, the tolerance may be widened to ±3 K up to 100°C, ±5 K from 100 °C to 200°C and ±10 K from 200°C to 315°C. When this is done, the tolerance used should be specified in the test report. The user should also specify the tolerance achieved at temperatures above 315 °C.
Thermal radiation
The ability of the specimen to transfer heat by thermal radiation shall be minimised. This will normally result in the screening of any heating or cooling elements from the specimen and ensuring that parts of the chamber surfaces are not significantly different in temperature from that of the conditioning air.
Mounting
The thermal conduction and other relevant characteristics of the mounting and connections of the test specimen should be specified in the relevant specification. When the test specimen is intended for use with specific mounting devices, these shall be used for testing.

If you are still interested in any kind of environmental test chambers, and I'm pleased provide some of our details and project to you. That's more, at present we have more attractive price for you. Welcome for inquiry any time, I will reply asap!
If you want to know more information about our products or our company, please feel free to contact sales@lenpure.com or visit http://www.lenpure.com/ .













