Environmental Test Chambers for LV124: Electric and Electronic Components in Passenger Cars up to 3.5t-General Requirements, Test Conditions and Tests-Part 2: Environmental Requirements
Adhere to high investment in the scientific research and creating differentiated environmental test chambers, Shanghai Lenpure company has gained lots of honor certificates thanks to its superior quality, design and performance which are widely praised by customers. Lenpure company climatic chambers win a number of software copyright and technology patents, combining reliability, easy-to-use performance with practicality to meet all-round requirements from customers.

With Overseas Business Department and corresponding After-sales Department set up, Lenpure company has advanced sales system and after-sales service system.
Lenpure company adheres to the development concept of Tests-for the purpose of progress and efficient end-to-end service system and vertical management structure, ensuring the policies from diversified and experienced management team are effective and in time. Persisting in innovation and excellent enterprise culture is our core competence. Based on the industry advantages and scientific innovation, Lenpure company will keep persisting in building up future-oriented environmental test chambers, to create value to customers and society.
This paper is intended as a general introduction to cyclic corrosion testing (CCT). It outlines the rationale for cyclic testing, includes some guidelines for using cyclic tests and explains some common CCT cycles and their applications. This discussion is not intended to be a complete, exhaustive tutorial on cyclic corrosion testing. Consult the referenced technical papers for more detailed information.
Salt spray was first used for corrosion testing around 1914. In 1939, the neutral salt spray test was incorporated as ASTM B117.1. This traditional salt spray specifies a continuous exposure to a 5% salt fog at 35℃. During the course of 80 years of use, there have been many modifications and refinements to B117. In spite of all these refinements, there has long been general agreement that “salt spray” test results do not correlate well with the corrosion seen in actual atmospheric exposures. Nevertheless, B117 has been generally accepted as the standard corrosion test method and is still widely specified for testing painted and plated finishes, military components and electrical components.
As the demand for improved corrosion protection increased, engineers and scientists attempted to develop test procedures to more accurately predict the corrosion of materials. In England, during the 1960’s and 1970’s, Harrison and Timmons2, 3 developed the cyclic test, which has been found especially useful for industrial maintenance coatings. More recently, the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) and The American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI) have been studying cyclic testing for automotive applications. Their progress has been encouraging and is well documented.4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 Japanese researchers have also developed a number of cyclic corrosion test methods.
Cyclic corrosion testing is intended to be a more realistic way to perform salt spray tests than traditional, steady state exposures. Because actual atmospheric exposures usually include both wet and dry conditions, it makes sense to pattern accelerated laboratory tests after these natural cyclic conditions. Research indicates that, with cyclic corrosion tests, the relative corrosion rates, structure and morphology are more similar to those seen outdoors. Consequently, cyclic tests usually give better correlation to outdoors than conventional salt spray tests. They are effective for evaluating a variety of corrosion mechanisms, including general, galvanic, and crevice corrosion.
Cyclic corrosion testing is intended to produce failures representative of the type found in outdoor corrosive environments. CCT tests expose specimens to a series of different environments in a repetitive cycle. Simple exposures may consist of cycling between salt fog and dry conditions. More sophisticated automotive methods call for multistep cycles that may incorporate immersion, humidity, condensation, along with salt fog and dry-off.
Originally, these automotive test procedures were designed to be performed by hand. Laboratory personnel manually moved samples from salt spray chambers to humidity chambers to drying racks, etc. More recently, microprocessor controlled chambers have been used to automate these exposures and reduce variability.
A brief introduction of the Environmental Test Chambers for LV124: Electric and Electronic Components in Passenger Cars up to 3.5t-General Requirements, Test Conditions and Tests-Part 2: Environmental Requirements
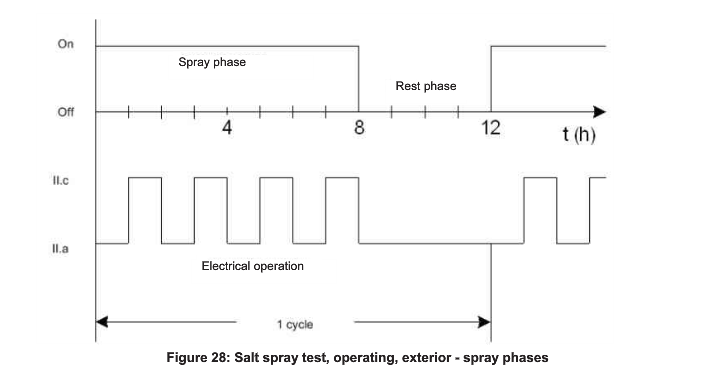
Salt Spray Test, operating exterior.
This test simulates the exposure of the component to air and water containing salt, a situation that may occur in certain areas of the world and at wintry road conditions The test is intended to verify the resistance of the component to malfunction when exposed to salt, e.g. due to short circuits and leakage currents caused by the ingress of salt into the component.
Test procedure:
| Operating mode of DUT |
D During spray phase: During spray phase: Intermitting between 1 h operating mode Il.a and 1 h operating mode Il.c. During rest phase: Operating mode Il.a |
| Test temperature | 35℃ |
| Test cycle | Each test cycle consists of an 8 h spray phase and a 4 h rest phase |
| Number of test cycle |
For components in the underbody/engine compartment: 12 cycles For other components: 8 cycles |
| Number of DUTs | 6 |
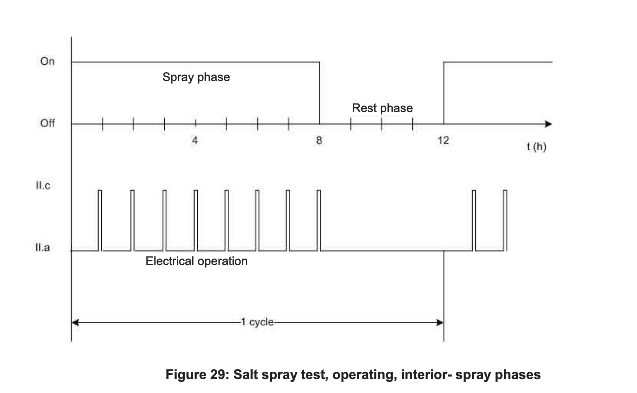
Salt Spray Test, operating interior
This test simulates the exposure of the component to air containing salt, as it may occur in certain areas of the world. The test is intended to verify the resistance of the component to malfunction when exposed to salt, e.g. due to short circuits and leakage currents caused by the ingress of salt into the components.
Test procedure:
| Operating mode of DUT |
D During spray phase: During spray phase: Intermitting between 55 mins operating mode Il.a and 5 mins operating mode Il.c. During rest phase: Operating mode Il.a |
| Test temperature | 35℃ |
| Test cycle | Each test cycle consists of an 8 h spray phase and a 4 h rest phase |
| Number of test cycle | 2 |
| Number of DUTs | 6 |
If you are still interested in any kind of environmental test chambers, and I'm pleased provide some of our details and project to you. That's more, at present we have more attractive price for you. Welcome for inquiry any time, I will reply asap!
If you want to know more information about climate chambers or our company, please feel free to contact sales@lenpure.com or visit http://www.lenpure.com/ .











