Climate Chambers for SAE J1879 : Handbook for robustness validation of semiconductor devices in automotive applications
The purpose of Shanghai Linpin Instrument Stock Co., Ltd. is to design to meet the demanding requirements for scientific and laboratory research. Advanced engineered design incorporates the latest in cabinet, refrigeration, temperature control and monitoring features.
Provides energy efficient, convenient, safe and reliable performance for optimal storage temperature environments necessary for a wide range of life science, pharmacy, biological, medical, clinical, and industrial applications. One of the most representative is the walk-in temperature and humidity test chamber.

The temperature and humidity test chamber is suitable for testing large samples such as vehicle and parts, tires, etc. The following is the Climate Chambers for SAE J1879 : Handbook for robustness validation of semiconductor devices in automotive applications standard.
This document will primarily address intrinsic reliability of electronic components for use in automotive electronics. Where practical, methods of extrinsic reliability detection and prevention will also be addressed. The current handbook primarily focuses on integrated circuit subjects, but can easily be adapted for use in discrete or passive device qualification with the generation of a list of failure mechanisms relevant to those components. Semiconductor device qualification is the main scope of the current handbook.
Other procedures addressing extrinsic defects are particularly mentioned in the monitoring chapter. Striving for the target of Zero Defects in component manufacturing and product use it is strongly recommended to apply this handbook. If it gets adopted as a standard, the term “shall’’ will represent a binding requirement.
This document does not relieve the supplier of the responsibility to assure that a product meets the complete set of its requirements.
Robustness Validation is a process by which to demonstrate the robustness of a semiconductor component under a defined mission profile. Robustness Validation represents an approach to qualification and validation that is based om knowledge of failure mechanisms and relates to specific Mission Profiles. The knowledge gained by applying this approach leads to improvement that extends beyond the component and its manufacturing process under consideration.
RV contains great potential for re-use, which contributes in its entirety to a significant increase in quality and reliability, time to market and reduction of costs. Last but not least, this will result in improvement of the competitiveness of all involved participants from the value adding chain.
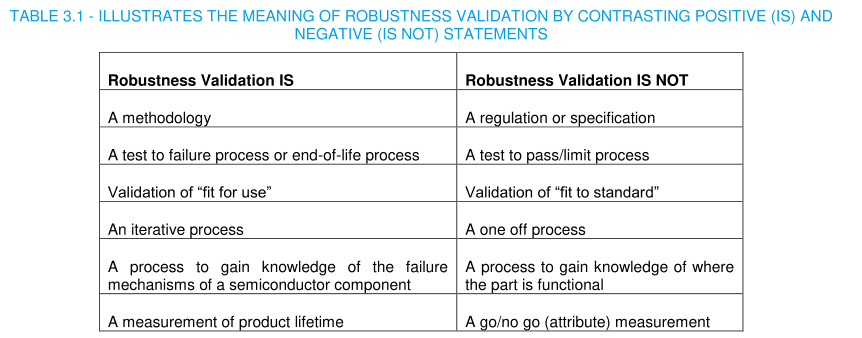
Robustness is the capability of functioning correctly or not failing under varying application and production conditions.Robustness Validation relies heavily on expertise and knowledge, and. therefore, requires detailed explanation and intensive communication among the specialists of the participants along the entire value adding chain.
This methodology is based on three key components:
l Knowledge of the conditions of use (mission profile, see section 5);
l Knowledge of the failure mechanisms and failure modes and the possible interactions between different failure mechanisms;
l Knowledge of acceleration models for the failure mechanisms needed to define and assess accelerated tests.
Robustness Validation is a knowledge-based approach [1,7,8] utilizing stress tests that are defined to address dedicated failure mechanisms using suitable test vehicles (e.g.. wafer test structures. packaged parts) and specific stress conditions.If accurately applied this approach results in a product being qualified as "fit for use", and not "fit for standard" only.
Results of Robustness Validation can be represented by the use of Robustness Diagrams.The Commodity Component Robustness Diagram, shown in figure 4.2, represents the first use of a robustness diagram, and is initiated at the conclusion of the finalization of the Mission Profile. At this point, the Semiconductor Component Supplier investigates whether the mission profile requirement can be achieved by using the relevant commodity device.
Figure 4.2 provides such a pictorial representation for two parameters, A and B, which have a certain relationship, such as voltage and temperature. Many parameters may be simple enough to plot one-dimensionally. The red box represents the area of the application's specification, which the commodity component must meet or exceed. The light blue area represents the commodity components actual performance.
The Robustness Margin is the distance between any point of application specification and the point of failure of the commodity component, taking into account all variations of the account all various of the product and the application's environment. The failure could result in different failure modes X, Y. Z. depending on the values of the parameters A and B. A robust component is a component that is able to maintain all the required characteristics under the conditions of use over the lifecycle without degradation to out-of spec-values.
The Commodity Component Robustness Diagram should be reviewed with the customer to demonstrate the actual robustness of the component when developing the application FMEA.
The Application-Specific Component Robustness Diagram, shown in figure 4.3, represents the second use of a robustness diagram and is initiated at the conclusion of the Robustness Validation Stress Test. At this point, the Component Supplier demonstrates to his customer the robustness of the semiconductor component to exceed the application specification requirement.
The IC specification for parameters A and B can be represented by a box (in blue) that displays the minimum and maximum allowed values. Naturally, the range of parameter values for a certain application must lie within this box.However, the specification limit does not imply that the product will fail at this point. Robustness Validation identifies the point of failure for the values of (A, B).
The line connecting all points of failure gives the component capability as shown by the light blue area. When any point (Ai, Bi) lies outside the component capability a failure criterion related to A, B or both parameters is violated and the semiconductor component fails. The type of failure mechanism that causes the failure.depends on the parameter values and can vary along this component capability curve. Examples for parameters A and B.are given in Table 4.2.
The robustness assessment must be done separately for each identified failure mechanism using the Knowledge Matrix when the potential risks and failure mechanisms for this qualification were assessed. Failure mechanisms that were not identified but did occur in the qualification will also be assessed for robustness. The robustness assessment is done by compiling a Robustness Diagram and comparing stress test and characterization data to the requirements.
If you are still interested in any kind of environmental test chambers, and I'm pleased provide some of our details and project to you. That's more, at present we have more attractive price for you. Welcome for inquiry any time, I will reply asap!
If you want to know more information about climate chambers or our company, please feel free to contact sales@lenpure.com or visit http://www.lenpure.com/ .











